
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business landscape, organisations rely on robust management frameworks to achieve their strategic goals and drive sustainable growth. Two essential disciplines that enable organisations to deliver results and outperform competitors are project management and operations management. While both focus on the effective use of resources, they serve different purposes within an organisation.
In this guide, we’ll provide an in-depth comparative analysis of project management versus operations management to help you determine the right approach for your needs.
Understanding About Project Management?
Project management involves the application of knowledge, tools, skills and techniques to execute projects effectively and efficiently. As defined by the Project Management Institute (PMI), project management is the “application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques applied to project activities to meet the project requirements.”
At its core, project management tackles unique, temporary endeavours with defined deliverables, timelines and goals. For example, launching a new product, constructing a building, organising a marketing campaign or developing custom software solutions are all projects. The overarching aim of project management is to achieve the end goals of the project while optimising budget, time and resources.
Unlike routine business operations, projects are temporary in nature and have a defined beginning and end. Once the objectives are met, the project team can be disbanded and resources reallocated elsewhere. The success of a project is determined by whether it achieves the intended outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction.
What Comes Under Operations Management?
In contrast to project management, operations management involves the administration and oversight of recurring daily business activities that produce products and services. It aims to increase efficiency and reduce costs in ongoing operations through optimal use of resources. Operations management focuses on predictable, routine processes that allow organisations to consistently deliver quality outputs.
Some examples of operations management activities include inventory control, supply chain coordination, quality assurance, production scheduling, and workflow optimization. While projects can be unique and dynamic, operations are typically standardised and repetitive to achieve consistency. Operations management ensures that these routine processes align with the organisation’s overall strategy.
The goal of operations management is to gain a competitive advantage by maximising productivity and efficiency while minimising operational costs. This is achieved by streamlining processes, eliminating bottlenecks, and leveraging automation and technology solutions. Operations managers oversee functional departments involved in production or service delivery to provide customers with the best experience possible.
Key Differences Between Project Management And Operations Management
While management is a universal function across all organisations, project management and operations management are distinct disciplines that serve unique purposes. Below we highlight the fundamental differences between the two approaches:
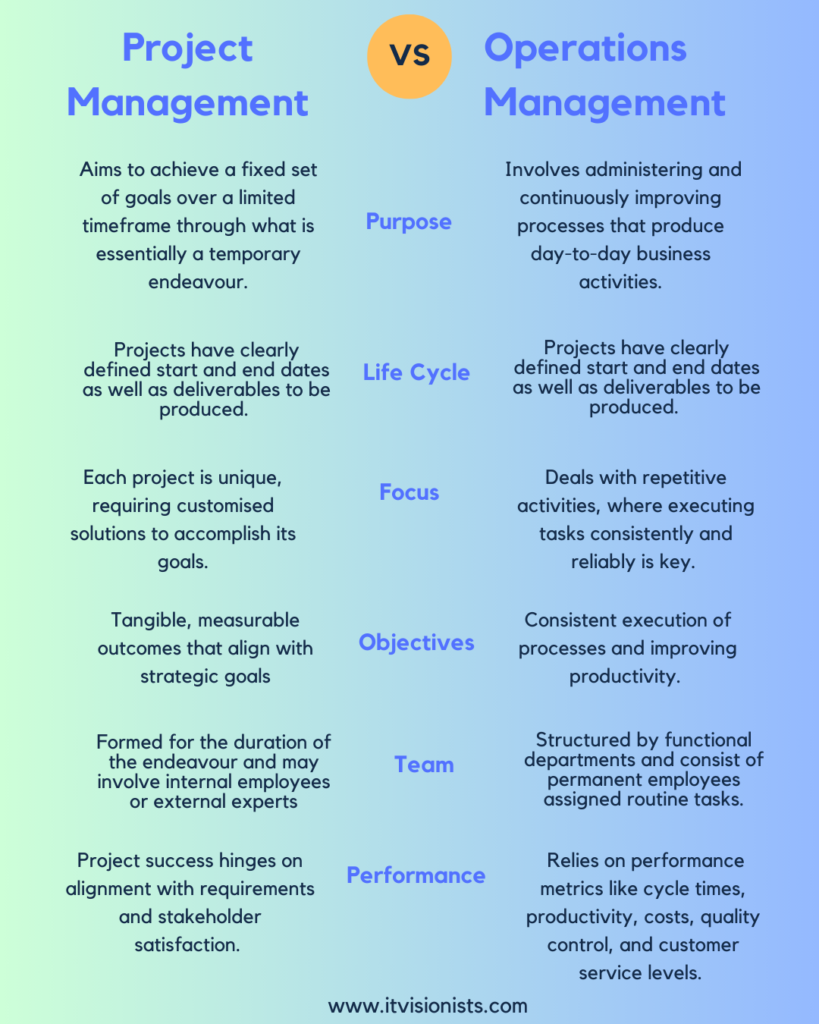
Nature And Purpose
Project management aims to achieve a fixed set of goals over a limited timeframe through what is essentially a temporary endeavour. Operations management involves administering and continuously improving processes that produce day-to-day business activities.
Duration And Lifecycle
Projects have clearly defined start and end dates as well as deliverables to be produced. The typical project lifecycle includes initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure stages. Operations are ongoing initiatives without a definite endpoint. The focus is on sustaining and optimising processes over time rather than completing temporary endeavours.
Focus On Uniqueness Vs. Repetition
Each project is unique, requiring customised solutions to accomplish its goals. This makes project management more dynamic and fluid. Operations management deals with repetitive activities, where executing tasks consistently and reliably is key. Standardisation enables economies of scale and reduced costs.
Objectives
Project objectives are tangible, measurable outcomes that align with strategic goals. Operations management focuses on consistent execution of processes and improving productivity. The overarching goal is to provide quality goods or services through streamlined workflows.
Team Composition
Project teams are formed for the duration of the endeavour and may involve internal employees or external experts. Operations teams are structured by functional departments and consist of permanent employees assigned routine tasks.
Risk And Uncertainty
The temporary and unique nature of projects often involves higher levels of risk and uncertainty. A major component of project management involves developing a risk management plan and anticipating contingencies. In operations, the focus is on stability, predictability and minimising disruptions through careful planning.
Performance Measurement
Project success hinges on alignment with requirements and stakeholder satisfaction. Operations management relies on performance metrics like cycle times, productivity, costs, quality control, and customer service levels. The goal is predictable, consistent processes.
Top Project Management Tools: Enhancing Efficiency And Collaboration
The right project management tools go a long way in enhancing team collaboration, optimising workflows, and ensuring successful delivery of projects. Given below are popular project management tools:
ClickUp
ClickUp offers powerful features for task management, collaboration, custom reporting, and data visualisation. It’s highly flexible and scalable for teams of all sizes.
Trello
Trello empowers teams to organise projects and manage tasks in a flexible, visual manner using customizable boards and lists. The simple drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to prioritise tasks and track progress.
Asana
Asana is a flexible work management platform suitable for managing anything from individual tasks to complex projects. Key features include task dependencies, milestones, project timelines, file sharing and reporting tools.
Monday.com
Monday.com provides an intuitive visual interface to streamline project planning and monitoring. Teams can create views tailored to their workflows and collaborate across departments and locations.
Jira
Jira is a robust project management tool designed for software teams. It offers advanced capabilities like customizable workflows, release planning, reporting, and project roadmapping.
Basecamp
Basecamp stands out for its ease of use, centralised communication, and functionalities for task management and file sharing. It’s ideal for small businesses and teams that value simplicity.
Wrike
Wrike is a comprehensive work management platform built for cross-functional collaboration, advanced scheduling, resource allocation, and real-time reporting across projects.
Best Operations Management Tools: Streamlining Productivity And Effectiveness
To optimise processes and build efficient operations, organisations rely on specialised operations management platforms and ERP systems. Here are some top operations management tools options:
SAP ERP
SAP ERP centralises operational data across departments including accounting, sales, HR, inventory and manufacturing. It facilitates forecasting, planning and enterprise reporting.
Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is an end-to-end cloud ERP solution suitable for financials, inventory, CRM, and business intelligence. It scales rapidly as needs grow.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 integrates powerful ERP, CRM and business analytics capabilities. It delivers actionable insights to streamline operations and drive productivity.
Odoo
Odoo offers a suite of business applications including project management, accounting, manufacturing, inventory and HR tools. It can be customised to fit your needs.
JDA Software
JDA offers solutions tailored for demand forecasting, supply chain planning, manufacturing optimization and transportation management.
Fishbowl Inventory
Fishbowl Inventory is designed specifically for handling inventory management, warehouse operations, and order management functionalities.
How Project Management And Operations Management Contribute To Business Success?
While project management and operations management have distinct purposes, they complement one another to create a robust management framework for overall business success.
Project Management’s Contribution
Effective project management ensures initiatives are delivered on time, within budget and fulfil quality standards. This builds credibility with stakeholders and enables the organisation to achieve strategic goals through successful projects.
Benefits Of Project Management
Project management provides several advantages including:
- Improved resource and cost optimization
- Enhanced collaboration and communication
- Proactive risk management resulting in on-time, on-budget delivery of projects
- Higher customer and stakeholder satisfaction levels
- Faster realisation of ROI on projects and strategic initiatives
Operations Management’s Contribution
Smooth operations and efficient processes are the bedrock of customer satisfaction and business profitability. Operations management optimises productivity levels and minimises disruptions to enable growth.
Benefits Of Operations Management
Operations management offers vital benefits:
- Increased efficiency through eliminating redundancies and bottlenecks
- Reduced operational costs and overhead expenses
- Improved productivity through workflow optimization
- Greater consistency resulting in higher quality of goods/services
- Data-driven insight for informed decision making
Synergy Between Project And Operations Management
Project and operations management work synergistically to turn strategy into reality. Efficient operations create capacity for organisations to undertake more projects and strategic initiatives. Successful projects also often enhance operations. The interplay between the two disciplines ensures long-term business success.
Industries And Applications
Project management is critical for companies in consulting, construction, IT, events, marketing, engineering and product development. Operations management is indispensable in manufacturing, supply chain, healthcare, transportation, retail, food service, and other operationally intensive sectors. While rarely used in isolation, purposefully leveraging project and operations management can optimise organisational performance.
Finding The Right Fit: Project Management Vs Operations Management
In conclusion, project management and operations management serve unique purposes within organisations. Project management provides the framework for executing strategic, temporary initiatives with specific deliverables and end goals. Operations management enables the smooth delivery of products and services through streamlined, repeatable processes.
While inherently different, both disciplines add immense value in their own right. The key is determining which approach fits your needs and leveraging their respective strengths. With robust project and operations management capabilities, organisations position themselves to respond to dynamic market landscapes, adopt innovation, meet customer expectations and become industry leaders. The complementary synergies between both drive growth and competitive advantage.
Key Takeaways: Project Management Vs Operations Management
- Project management deals with unique initiatives to accomplish defined goals and deliverables. Operations management oversees ongoing, repetitive processes to provide consistent outputs.
- Project management aims to optimise time, budget and resources to successfully complete projects. Operations management focuses on reliability, efficiency and productivity improvements.
- Project teams are assembled for temporary endeavours then disbanded upon completion. Operations teams are structured by functional departments and meant for long-term roles.
- Projects carry uncertainty and risks that must be mitigated through planning. Operations management minimises disruptions through standardised processes.
- Project success depends on aligning deliverables to requirements. Operations management hinges on metrics like cycle times, costs, and quality.
- Robust project and operations management capabilities enable organisations to thrive in dynamic markets and drive growth.
The key differences between project and operations management were highlighted along with the value each approach delivers. Top tools and real-world applications were also provided. This guide can help managers determine the right framework for their business needs and leverage both disciplines for maximum impact.
